
NumPy arange() method in Python AskPython
The NumPy arange () function has only a single required parameter: the stop parameter. By default, NumPy will start its sequences of values beginning at 0 and increasing by 1. When you pass in a single number, the values will increase from 0, up to (but not including) the value, incrementing by 1.

Python numpy.arange() With Examples [Latest] All Learning
NumPy offers a lot of array creation routines for different circumstances. arange () is one such function based on numerical ranges. It's often referred to as np.arange () because np is a widely used abbreviation for NumPy.

Quick Tutorial for Python Numpy Arange Functions with Examples MLK Machine Learning Knowledge
numpy.arange¶ numpy. arange ([start, ] stop, [step, ] dtype=None, *, like=None) ¶ Return evenly spaced values within a given interval. Values are generated within the half-open interval [start, stop) (in other words, the interval including start but excluding stop).For integer arguments the function is equivalent to the Python built-in range function, but returns an ndarray rather than a list.

NumPy arange() A Simple Illustrated Guide Finxter
Here's a simple example: import numpy as np array = np.arange (start=0, stop=10, step=2) print (array) # Output: # array ( [0, 2, 4, 6, 8]) In this example, we import the numpy module and use the np.arange function to create an array. The start value is 0, the stop value is 10, and the step value is 2.
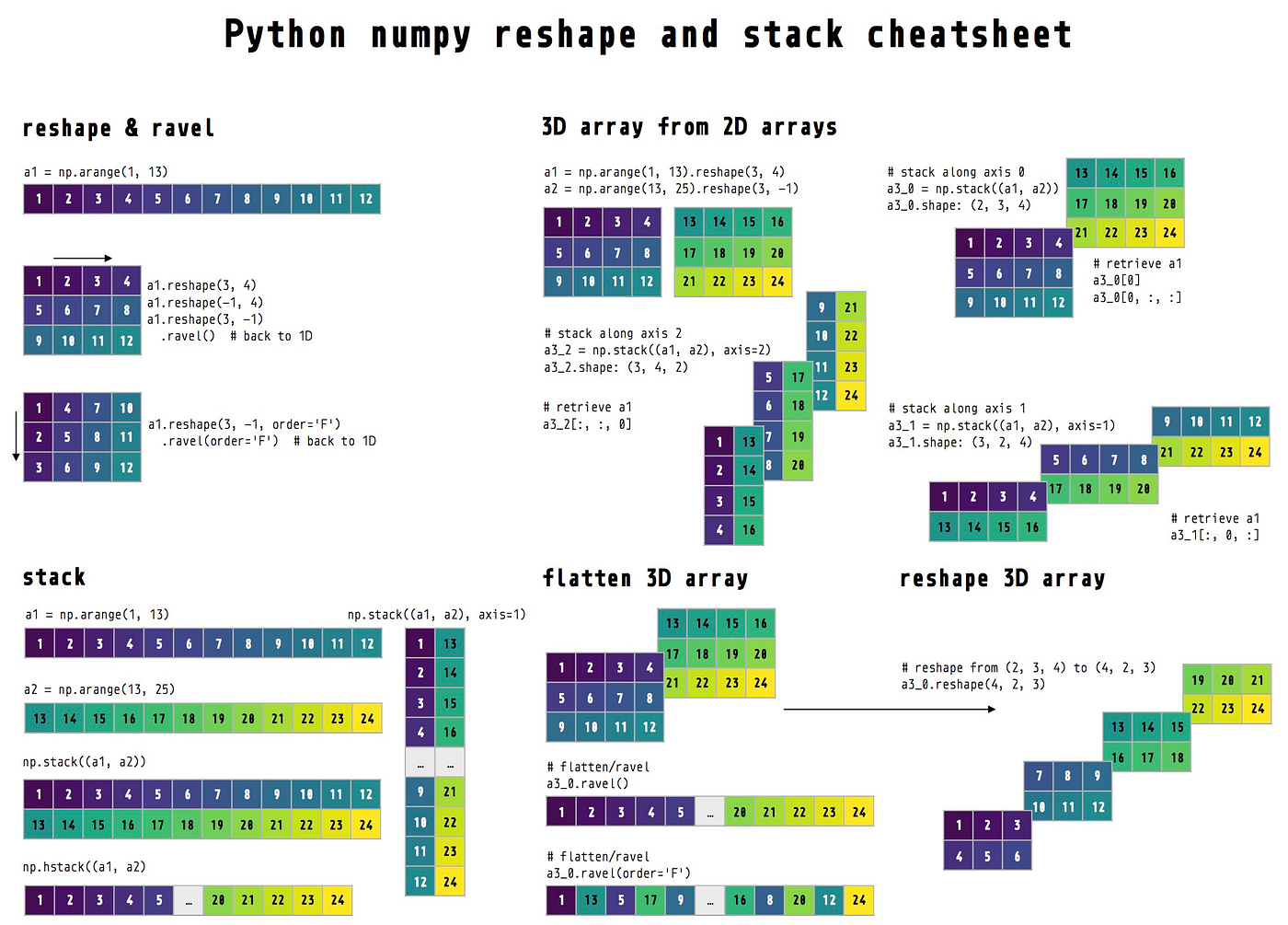
Reshape numpy arrays—a visualization Towards Data Science
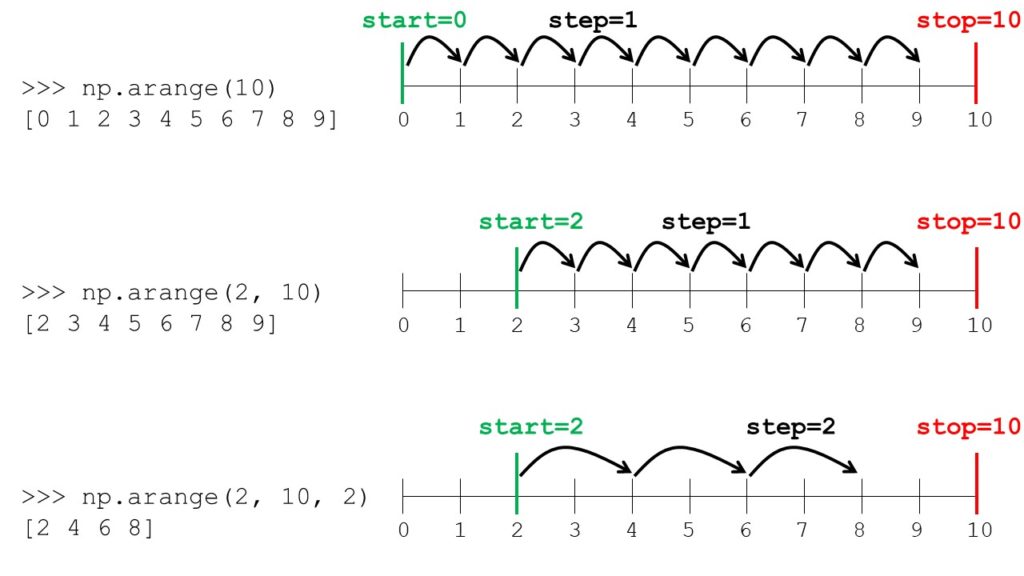
Start of interval. The interval includes this value. The default start value is 0. stopinteger or real End of interval. The interval does not include this value, except in some cases where step is not an integer and floating point round-off affects the length of out. stepinteger or real, optional Spacing between values.

numpy.ones() in Python DigitalOcean
Returns arangendarray Array of evenly spaced values. For floating point arguments, the length of the result is ceil ( (stop - start)/step). Because of floating point overflow, this rule may result in the last element of out being greater than stop. Warning The length of the output might not be numerically stable.
NumPy arange() A Simple Illustrated Guide Be on the Right Side of Change
Example import numpy as np # create an array with elements from 5 to 10 array1 = np.arange ( 5, 10) print(array1) # Output: [5 6 7 8 9] Run Code arange () Syntax The syntax of arange () is: numpy.arange (start = 0, stop, step = 1, dtype = None) arange () Argument The arange () method takes the following arguments:
Python NumPy Array Learn NumPy Arrays with Examples Learntek
NumPy offers a lot of array creation routines for different circumstances. arange () is one such function based on numerical ranges. It's often referred to as np.arange () because np is a widely used abbreviation for NumPy.

NumPy arange() How to Use np.arange() Real Python
The numpy.arange () function in Python's NumPy library is used to generate arrays of evenly spaced values within a specified range. It's similar to Python's built-in range () function but produces a NumPy array as output.

[Ultimative Guide] The Numpy Arange Function Simply Explained YouTube
The NumPy arange function returns evenly spaced numeric values within an interval, stored as a NumPy array (i.e., an ndarray object). That might sound a little complicated, so let's look at a quick example. We can call the arange () function like this: numpy.arange (5) Which will produce a NumPy array like this: What happened here?

How to Use Python NumPy arange() Function
The numpy arange () function creates a new numpy array with evenly spaced numbers between start (inclusive) and stop (exclusive) with a given step: numpy.arange (start, stop, step, dtype= None, *, like= None) Code language: Python (python) For example, the following uses arange () function to create a numpy array: import numpy as np a = np.

Using the numpy arange() method Data Science Parichay
The advantage of numpy.arange () over the normal in-built range () function is that it allows us to generate sequences of numbers that are not integers. Example: Python3 import numpy as np print(np.arange (1, 2, 0.1)) Output: [1. 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9] If you try it with the range () function, you get a TypeError.
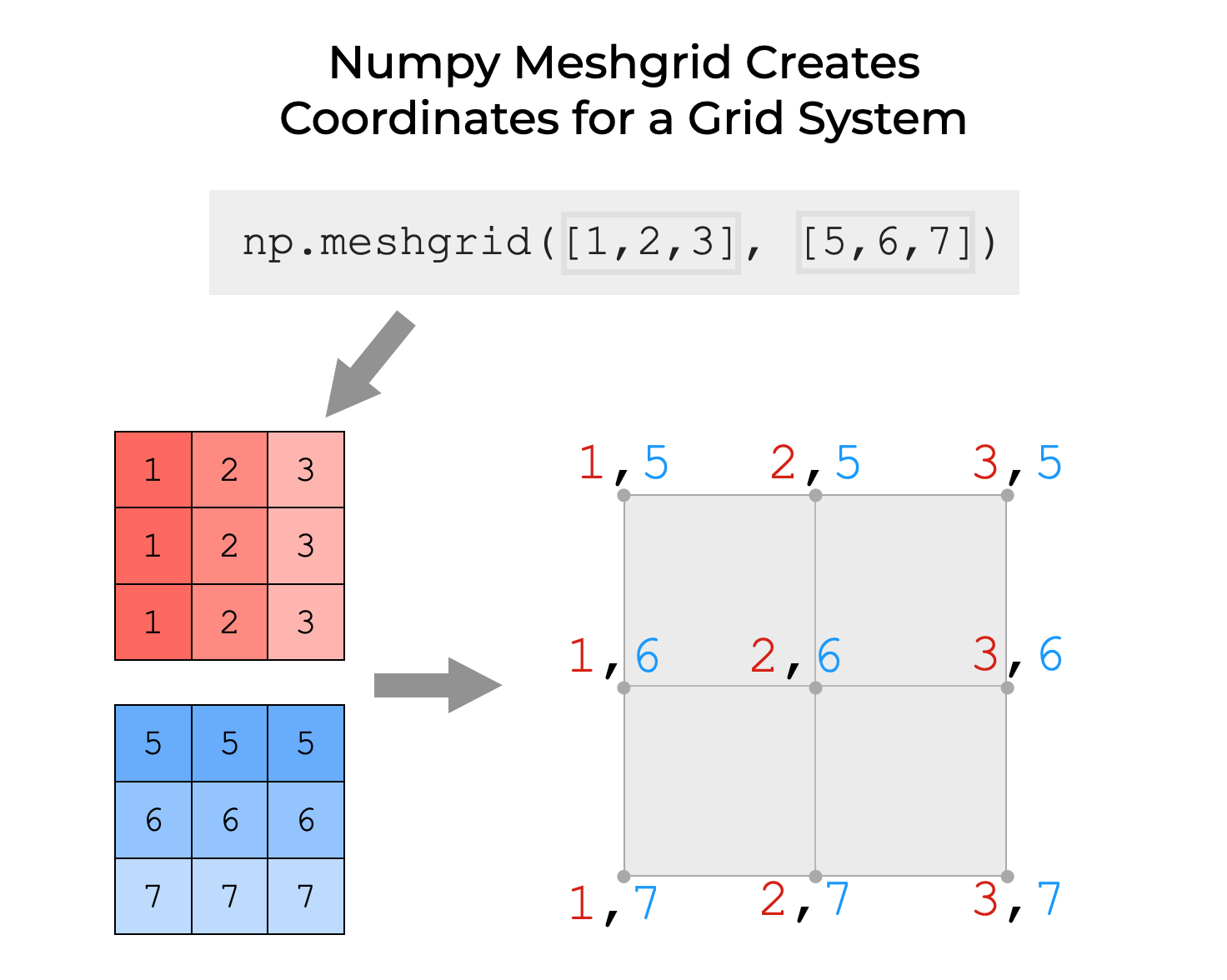
Numpy Meshgrid, Explained Sharp Sight
Let's consider a few examples: np.arange(0,10) #Returns array ( [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]) np.arange(-5,5) #Returns array ( [-5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4]) np.arange(0,0) #Returns array ( [], dtype=int64) It is possible to run the np.arange () method while passing in a single argument.
NumPy arange() Complete Guide (w/ Examples) • datagy
The Numpy Arange function is used to create a numpy array whose elements are evenly distributed within a given range. In this tutorial, we will understand the syntax of np.arange () and go through multiple examples by using its various parameters. Numpy Arange : numpy.arange () Syntax numpy.arange (start=0, stop, step=1, dtype)
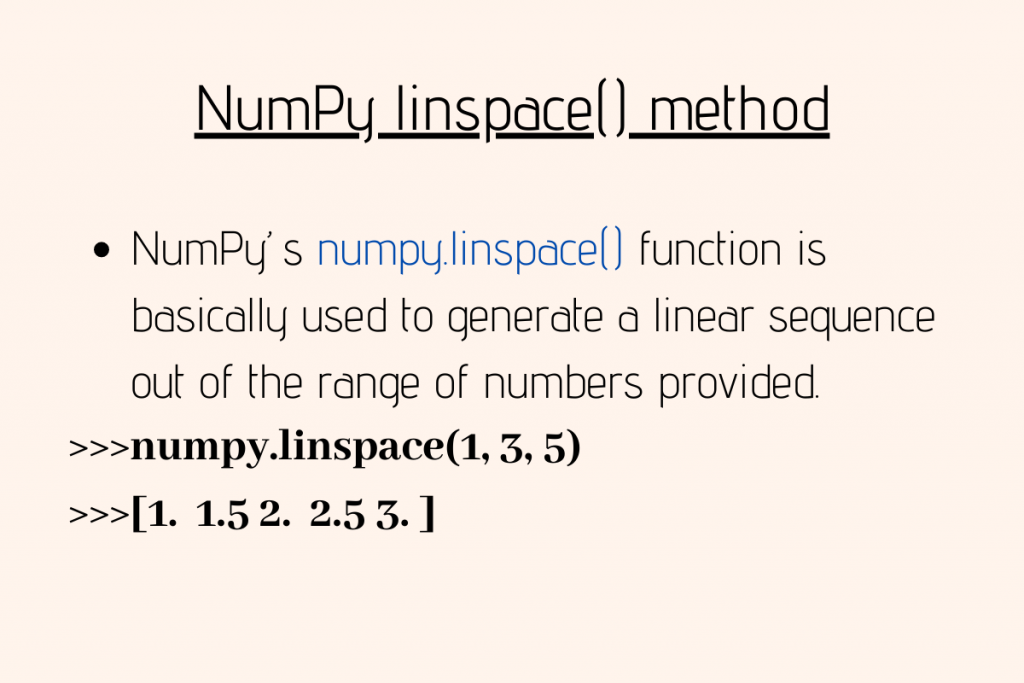
Numpy linspace() method AskPython
What's the NumPy Arange Function? The np.arange ( [start,] stop [, step]) function creates a new NumPy array with evenly-spaced integers between start (inclusive) and stop (exclusive). The step size defines the difference between subsequent values. For example, np.arange (1, 6, 2) creates the NumPy array [1, 3, 5].
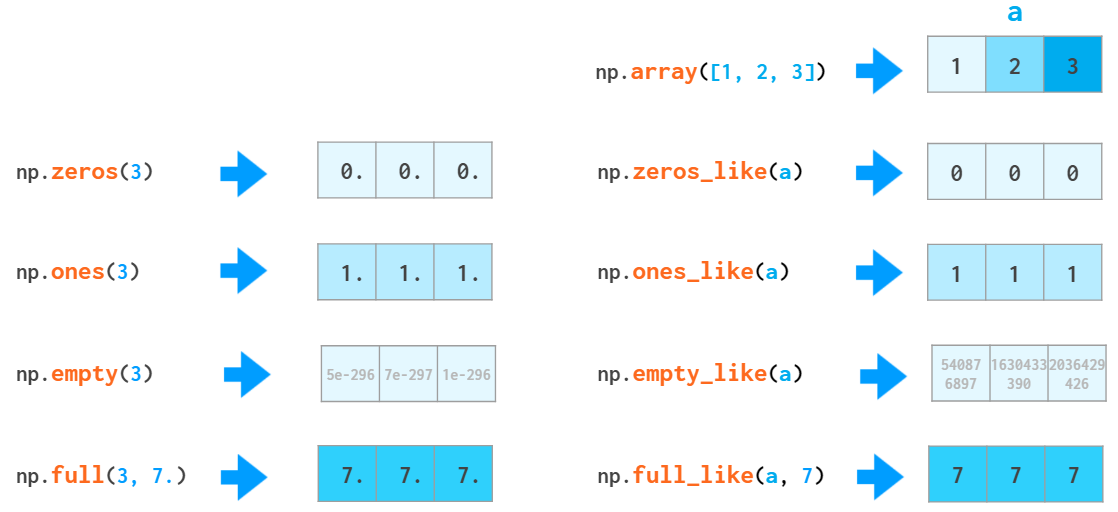
NumPy Illustrated The Visual Guide to NumPy by Lev Maximov Better Programming
5 Code examples of arange () NumPy Function Let's now understand the arange () function with code examples. For that, we'll first import Python NumPy. See below: import numpy as np Ex.1 NumPy Array with no Starting Point (Stop) We'll just provide one parameter to the arange function which will take it as an ending point. See below: np.arange (5)